what is the minimum temperature to safely hold hot food
In commercial foodservice, understanding nutrient safety temperatures is crucial to protecting your guests from foodborne affliction. All operators and food handlers are responsible for recognizing the importance of the temperature danger zone and should be educated to perform established nutrient safety procedures. Keep reading to learn all about the food temperature danger zone, how long food can safely stay in the danger zone, and the food safe temperature range for hot and cold food.
Shop All Kitchen Thermometers
Click below to learn about the temperature danger zone:
- Why Is the Danger Zone Important?
- How Long Food Can Stay in the Danger Zone
- How to Hold Cold Food
- How to Agree Hot Food
- Safe Cooking Temperatures
- How to Rapidly Cool Hot Foods
- Common cold Food Storage Times
What Is the Danger Zone?
The danger zone refers to the temperature range in which bacteria growth occurs well-nigh speedily on food. According to ServSafe recommendations, food temperatures between 41 and 135 degrees Fahrenheit correspond this danger zone. Leaner can multiply at whatever temperature inside the danger zone, but temperatures betwixt 70 and 125 degrees Fahrenheit provide the virtually hospitable environment for bacteria to thrive. The longer food sits in the temperature danger zone, the greater the risk that bacteria will grow on the nutrient.

Why Is the Temperature Danger Zone Important?
When foods are allowed to enter the temperature danger zone, leaner may grow to unhealthy levels and crusade the food to spoil. Dangerous leaner growth like this may occur without any visible signs that the food is unsafe for consumption. Foods may olfactory property and appear normal, but could really contain harmful amounts of bacteria that will cause foodborne affliction.
This is what makes the temp danger zone extremely important. As a nutrient service professional, it's your responsibility to go along foods out of the danger zone by using approved methods to chill, heat, and store foods.
What Is Fourth dimension Temperature Abuse?
Fourth dimension temperature corruption is the act of allowing foods to stay in the temperature danger zone of 41 to 135 degrees Fahrenheit. Forth with cross-contagion, time temperature abuse is a common source of foodborne illness. Foods may go time-temperature abused in three means:
- Foods are not held or stored at food safety temperatures
- Food is not cooked or reheated to the temperature required to eliminate possible pathogens
- Hot nutrient is non cooled properly before beingness placed in cold storage
What Are TCS Foods?
TCS stands for fourth dimension/temperature control safety. Foods that require strict time and temperature control are considered TCS foods. Pathogens love TCS foods considering they present an ideal environs for germs to grow and spread. Preventing TCS foods from inbound the danger zone and becoming time-temperature abused is a critical food rubber exercise. These are the high-risk TCS foods that should be closely monitored at all times:
- Milk and dairy products
- Meat and poultry
- Fish, shellfish, and crustaceans
- Trounce eggs
- Baked potatoes
- Cooked rice, beans, and vegetables
- Tofu, soy protein, or other plant-based meat alternatives
- Sprouts and sprout seeds
- Cut tomatoes, melons, and leafy greens
- Untreated garlic and oil mixtures
Back to Summit
How Long Can Food Stay in the Temperature Danger Zone?
ServSafe states that four hours is the maximum length of time ready-to-eat foods can stay in the temperature danger zone. After the 4 hour limit, foods must be thrown away. Within the 4 hour time limit, foods can be consumed, reheated, or chilled to bring them dorsum to nutrient safe temperatures. Checking temps every 2 hours allows for a greater window to perform any corrective actions that are necessary.
How to Proceed Nutrient Out of the Danger Zone
Kitchen thermometers are the fundamental to keeping foods out of the temp danger zone. By monitoring and recording food temperatures regularly, you tin forbid foods from becoming time-temperature abused. This is imperative while prepping, cooking, and holding nutrient on your buffet line or salad bar.
Follow these important tips to ensure you're making the all-time use of your kitchen thermometers to keep food safe for consumption.
- Always use the right type of thermometer for the chore.
- Never rely on the temperature display of your equipment lone.
- Place a thermometer inside your refrigerator or freezer as an additional prophylactic measure.
- Keep a written record of all temperature checks that includes the temp, the fourth dimension, and the proper noun of the operator.
- Clean and calibrate thermometers often.
Back to Top
Food Belongings Temperature
Once your food is cooked to the proper internal temperature or chilled to twoscore degrees Fahrenheit or beneath, it'south important to maintain these safe temperatures earlier serving. In that location are a number of instances in which foodservice professionals demand to concur food for extended periods of times. These instances could include holding food in salad confined and buffet lines or transporting food to off-site locations and catering events.
When transporting food, it is recommended you apply a food pan carrier or insulated catering bag to ensure your hot or cold foods remain safe for consumption.
Common cold Holding Temperature
The cold holding temperature for TCS foods must be at forty degrees Fahrenheit or below. Here are some tips to properly hold cold foods so they don't fall into the danger zone:
- Ensure your cold-belongings equipment keeps foods at 40 degrees Fahrenheit and below.
- Any cold nutrient held without refrigeration is safe for up to vi hours, starting from the time information technology was removed from refrigeration at 40 degrees Fahrenheit and below.
- Bank check the temperature of cold foods every 2 hours and discard whatever cold food that reaches a temperature of 70 degrees Fahrenheit or higher.
How Cold Does a Salad Bar or Refrigerator Have to Be to Proceed Nutrient Rubber?
Salad bars and refrigerators need to maintain temperatures at 40 degrees Fahrenheit and below to preclude the growth of dangerous leaner. This is especially important as y'all house vulnerable TCS foods including cheese, yogurts, meats, salad dressings, and egg products.
Belongings Temperature For Hot Food
The appropriate belongings temp for hot foods is 135 degrees Fahrenheit or above. Here are some tips to keep hot foods out of the danger zone:
- Never use hot belongings equipment to reheat nutrient. Foods should be heated to condom temperatures prior to holding. Hot holding equipment is designed to maintain current temps, not bring nutrient up to temp.
- When possible, keep food covered to help maintain temperatures and keep contaminants out.
- Stir frequently to distribute estrus throughout the food.
- Use the appropriate thermometer to monitor nutrient temperatures oftentimes.
- Discard hot food that has been sitting beneath 135 degrees Fahrenheit for more than 4 hours.
- Never mix freshly prepared food with foods already being held for service to forestall cross contagion.
How Often Should I Check the Temperature of Hot or Cold Holding Food?
It is recommended y'all bank check the temperature of your hot or cold belongings food every four hours. Withal, if y'all check every 2 hours instead, this allows enough time to have corrective activity in the outcome that food has fallen into the danger zone. By staying on top of your food's internal temperatures, y'all can prevent the spread of dangerous bacteria and eliminate food waste product past but re-heating or re-chilling the affected foods earlier bacteria has time to spread.
Back to Top
Safety Cooking Temperatures
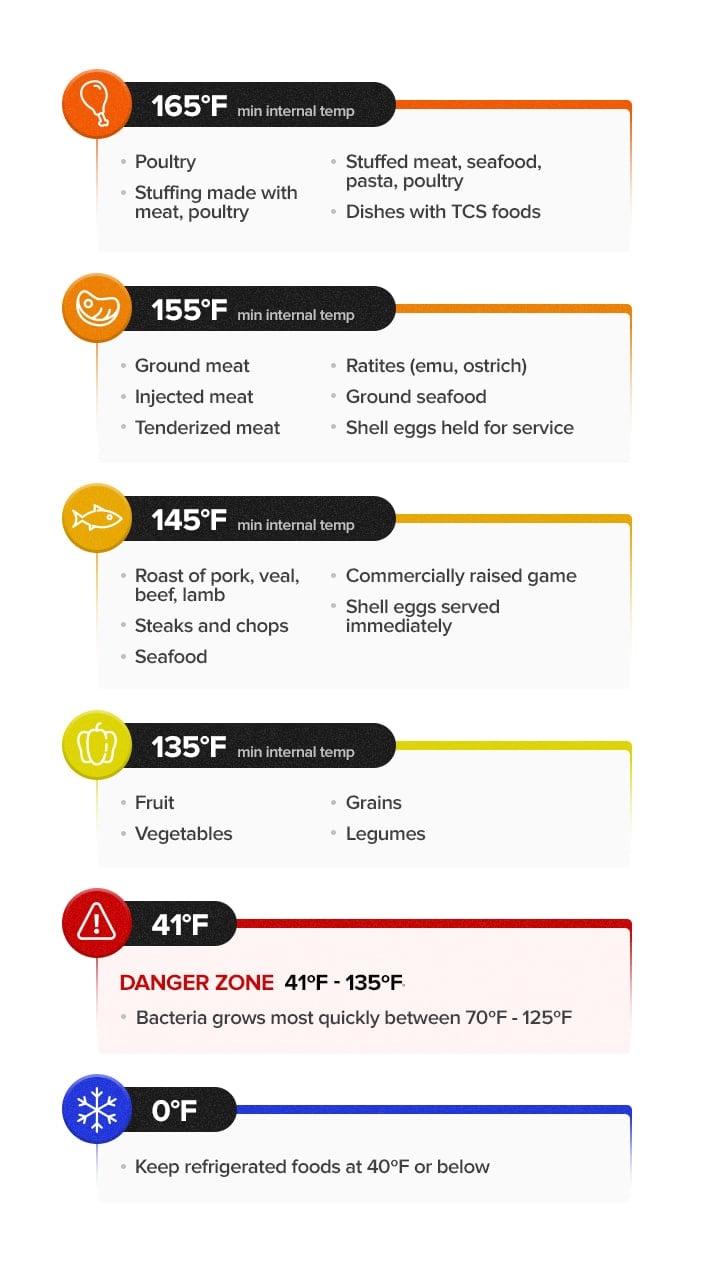
To prevent the spread of salmonella, staphylococcus aureus, listeria, and other dangerous bacteria, information technology'south important to monitor the internal temperature of the foods y'all serve. Follow the recommendations below for safe cooking temperatures of mutual TCS foods.
Melt to 165 degrees Fahrenheit for at least 15 seconds:
- Poultry, whole or ground
- Stuffing made with poultry, meat, or fish
- Blimp pasta, meat, poultry, or seafood
- Whatever dish that contains a cooked TCS food
Melt to 155 degrees Fahrenheit for at least 15 seconds:
- Ground beef, pork, or other meats
- Flavor-injected meats
- Tenderized meats
- Ratites (ostrich, emu)
- Ground, chopped, or minced seafood
- Eggs from the trounce, held for service
Cook to 145 degrees Fahrenheit for at to the lowest degree 15 seconds:
- Seafood
- Steaks and chops (beef, pork, veal, lamb)
- Commercially raised game
- Eggs from the shell, served immediately
- Roasts of beef, pork, veal, lamb (must be cooked for at to the lowest degree 4 minutes)
Melt to 135 degrees Fahrenheit (no minimum time):
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Rice, pasta, and other grains
- Legumes
Click below to print a visual reminder of the safe cooking temperatures listed to a higher place:
Printable Version
Dorsum to Peak
What Exercise You Demand to Know About Resting Time for Meats?
Before taking temperatures, it's important to note the balance time of meat required when removing it from the grill, oven, or other heat source. During this fourth dimension, the temperature will remain consequent or proceed to rise. This process helps to destroy harmful germs.
How Exercise You Rapidly Cool Hot Foods?
Many institutions and large commercial kitchens prepare dishes alee of time for maximum efficiency in their kitchen. The food is then cooled downward and held until service. When doing this, it's important to cool the food rapidly and safely and so that information technology doesn't linger in the danger zone for too long.
If y'all're preparing food alee of fourth dimension, you must bring the temperature downward to twoscore degrees Fahrenheit or below within ii hours of hitting its proper internal temperature.
Tips for Cooling Hot Foods to Food Safe Temperatures
Placing hot nutrient directly into your refrigerator or freezer is never recommended because it endangers the food around it by raising the ambient temperature in your fridge or freezer. This creates the possibility of other foods in your refrigerator or freezer entering the temperature danger zone and developing bacteria without you even knowing. Instead, follow these tips for chop-chop cooling your hot foods.
- Use a commercial blast chiller to cool foods chop-chop and minimize the time food spends in the danger zone.
- Store foods in shallow containers to permit the temperature to distribute more evenly.
- Consider using a cooling paddle to reduce the temperature of hot liquids including soups, stews, and sauces.
- Create an ice bath by filling a pot, container, or sink basin with ice. Containers of hot foods can be placed in the water ice bath to quickly absurd food to 40 degrees Fahrenheit or below.
Learn more than about bringing foods down to temperature in our cooling foods guide.
Cold Food Storage
In add-on to belongings and serving cold foods, it's important to know how long yous can shop common cold foods before they become unsafe for consumption. Ever engagement characterization your refrigerated foods and utilize a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system. Utilise this chart as a reminder of how long items can be safely kept before they must be discarded.
| Food Item | Fridge (xl°F) | Freezer (0°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Salary | 1 week | 1 month |
| Beverages | 3 weeks unopened, 7-10 days opened | 8-12 months |
| Cheese - hard (Swiss) | 3-four weeks | 6 months |
| Cheese - soft (brie) | i calendar week | 6 months |
| Craven, egg, macaroni, and tuna salad | 3-4 days | Practise non freeze |
| Cottage cheese | 1 week | Do non freeze |
| Dough - cookie | Use past date | 2 months |
| Dough - tube cans of rolls, biscuits, pizza dough | Apply by appointment | Do not freeze |
| Egg substitutes - opened | 3 days | Do not freeze |
| Egg substitutes - unopened | three days | 1 year |
| Eggs - fresh in crush | three-v weeks | Practice not freeze |
| Eggs - hard cooked | 1 week | Do not freeze |
| Fish - fatty (salmon) | 1-ii days | 2-three months |
| Fish - lean (cod) | 1-2 days | 6 months |
| Ground meats - raw | ane-two days | iii-four months |
| Ham - fully cooked, slices | 3-iv days | 1-2 months |
| Ham - fully cooked, whole | 1 week | 1-2 months |
| Hot dogs - opened | 1 week | 1-2 months |
| Hot dogs - unopened | 2 weeks | 1-ii months |
| Luncheon meats - opened | 3-v days | 1-2 months |
| Luncheon meats - unopened | ii weeks | 1-ii months |
| Margarine | 4-v months | 12 months |
| Mayonnaise - opened | two months | Do non freeze |
| Milk | one calendar week | 3 months |
| Poultry - cooked | 3-4 days | 2-6 months |
| Poultry - fresh, chicken or turkey | one-two days | 6 months |
| Prepared leftovers | iii-4 days | 2-3 months |
| Sausage - raw | one-two days | 1-two months |
| Sausage - cooked | ane calendar week | i-ii months |
| Steaks, chops, and roasts - raw | three-5 days | 4-6 months |
Back to Top
It'due south every food service operator'southward top priority to keep the food they're serving safe for consumption. Post-obit these important tips and guidelines will ensure your managers and staff have the knowledge to keep nutrient out of the danger zone, take corrective activity, and keep customers condom from harmful foods.
Source: https://www.webstaurantstore.com/article/29/following-food-safety-temperatures.html
0 Response to "what is the minimum temperature to safely hold hot food"
Post a Comment